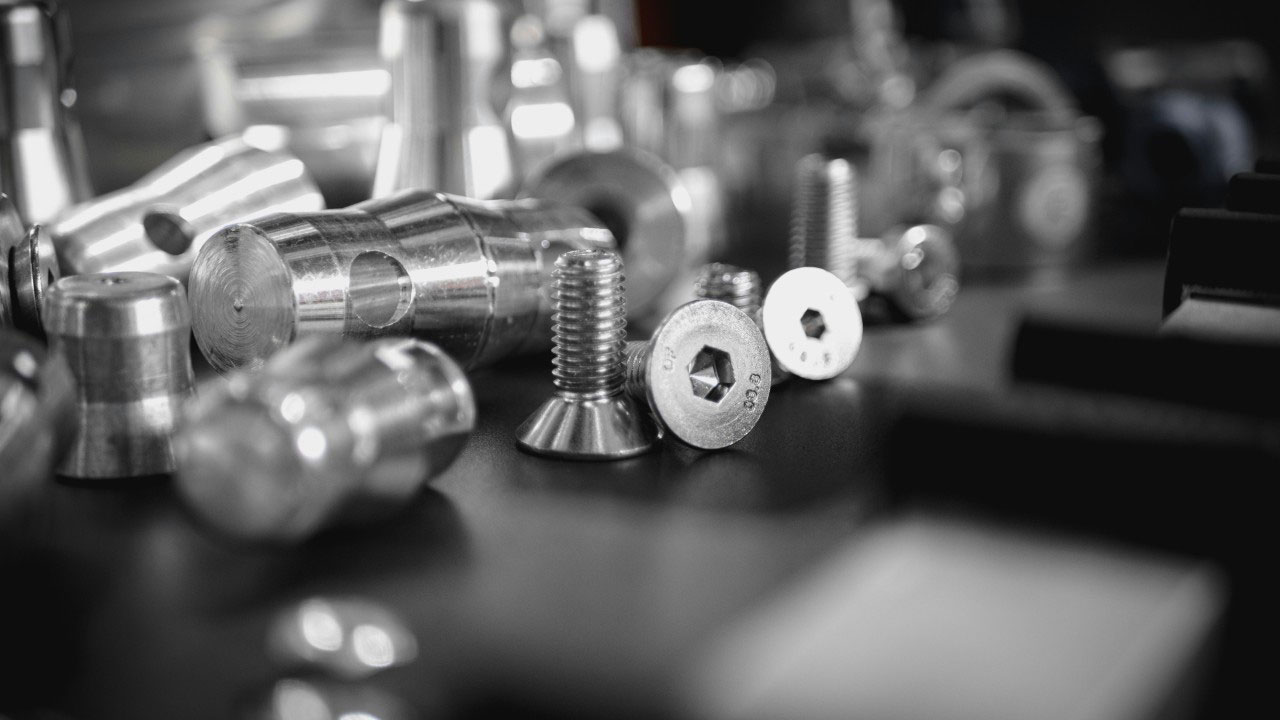
In the automotive industry, the demand for lightweight components has never been higher. The push for greater fuel efficiency, better performance, and enhanced environmental sustainability has driven manufacturers to rethink materials used in vehicle production, especially in critical parts like fasteners. Among the most popular lightweight materials are titanium and aluminum alloy. Both have their strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right material for fasteners depends on the specific needs of each application.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between titanium and aluminum alloy fasteners, comparing their mechanical properties, cost, and suitability for various applications, all while helping automotive manufacturers make informed decisions.
1. Titanium Fasteners: Strength and Durability
Titanium is known for its superior strength-to-weight ratio. It’s stronger than aluminum, and yet significantly lighter than steel. This makes titanium fasteners an attractive choice for high-performance vehicles, particularly in applications that require excellent fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance.
Advantages of Titanium:
Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Titanium’s strength is approximately 60% greater than aluminum, making it ideal for high-stress applications where strength is crucial. This is particularly important in areas like engine components, suspension parts, or any other application where safety and performance are a top priority.
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium’s natural oxide layer provides excellent protection against corrosion, even in harsh environments, such as those found in high-performance or off-road vehicles.
Durability: Titanium fasteners can withstand higher temperatures than aluminum alloy, which is particularly beneficial in engine and exhaust systems where high thermal resistance is required.
Longevity: Due to its resistance to wear, titanium fasteners tend to have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for replacements and repairs in the long run.
Challenges with Titanium:
Cost: Titanium is more expensive than aluminum, both in terms of material cost and manufacturing complexity. This can make titanium fasteners less viable for mass production, especially in cost-sensitive applications.
Machinability: Titanium is more difficult to machine than aluminum, requiring specialized equipment and increased processing time. This can result in higher production costs and lead times.
2. Aluminum Alloy Fasteners: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Aluminum alloys are widely used in the automotive industry due to their low weight and relatively low cost. Aluminum is especially popular for use in mass-market vehicles where cost efficiency is critical, and reducing weight without compromising too much on strength is essential.
Advantages of Aluminum Alloy:
Lightweight: Aluminum alloys are lighter than titanium, making them an ideal choice for weight-sensitive applications like automotive body parts, interior components, and trim. Reducing the overall weight of the vehicle directly contributes to better fuel efficiency and overall performance.
Cost-Effective: Aluminum is more affordable than titanium, both in terms of raw materials and manufacturing costs. This makes aluminum alloys an attractive option for high-volume applications where cost is a significant factor.
Good Corrosion Resistance: While not as corrosion-resistant as titanium, aluminum alloys still provide good resistance to rust and corrosion, particularly when treated or coated. This makes them suitable for many automotive applications, especially in moderate environments.
Ease of Machining: Aluminum alloys are easier to machine and form than titanium, which allows for quicker production times and lower manufacturing costs.
Challenges with Aluminum Alloy:
Lower Strength: While aluminum alloys are strong, they don’t offer the same strength-to-weight ratio as titanium. This makes aluminum alloys less suitable for high-stress applications where maximum strength is necessary.
Thermal Resistance: Aluminum has a lower melting point than titanium, making it less suitable for applications exposed to extreme heat, such as in exhaust systems or high-performance engine components.
3. Choosing the Right Material for Automotive Fasteners
When it comes to choosing between titanium and aluminum alloy for fasteners, the decision ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application. For high-performance and high-stress applications, titanium fasteners offer unparalleled strength and durability. However, they come at a higher cost, which may not be feasible for mass-market production or applications where weight is less of a concern.
On the other hand, aluminum alloy fasteners provide a more cost-effective solution without compromising much on weight. They are perfect for applications where weight savings are important, but extreme strength is not a critical requirement. Additionally, aluminum alloys are ideal for applications where ease of machining and lower production costs are a priority.
4. Key Applications for Both Materials
Titanium Fasteners:
Aluminum Alloy Fasteners:
5. Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Automotive Fasteners
In conclusion, both titanium and aluminum alloy have their place in the automotive industry, and the choice between the two largely depends on the specific requirements of the vehicle and its components. Titanium offers strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, but comes at a higher cost, making it suitable for high-performance and high-stress applications. Aluminum alloys, on the other hand, provide an affordable, lightweight solution for mass-market vehicles without sacrificing too much on strength.
For automotive manufacturers looking to optimize their supply chain, working with a reliable supplier who understands the nuances of these materials can help make the decision process smoother and more efficient. Whether you are designing a high-end sports car or working on a cost-effective production line, selecting the right fastener material is critical to achieving the perfect balance of performance, cost, and weight.
NAVIGATION





.png)
